Compressive strength is a fundamental parameter that informs the safety, quality and durability of a particular mix of concrete. Testing according to ASTM C39 is central to the QA/QC process.
For over 80 years, ASTM C39 has been the industry standard test method for testing the compressive strength of concrete cylinder specimens. In this article, we cover the basics, including:
- The importance of ASTM C39
- Recommended ASTM C39 supplies and equipment
- Test procedure and results
The Importance of ASTM C39 for Compressive Strength Testing
ASTM C39 is the standard test method for compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens. The standard outlines procedures for subjecting cylindrical concrete specimens to axial compressive forces until failure occurs. The strength of a cylinder is calculated by dividing the load at failure by the cross-sectional area of the cylinder, resulting in a stress value, referred to as the strength.
A concrete cylinder is a cylindrical specimen that is cast, molded and cured from fresh concrete in the field. Concrete cylinders can also be created by drilling cores from in-place concrete of an existing structure, but drilling a core specimen is typically a last and least desirable resort.
The results of ASTM C39 are used as a basis for concrete specification compliance and quality control, including aspects like proportioning, mixing and placing operations. According to ACI Code-318-19(22), “Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete and Commentary (Reapproved 2022),” a strength test for acceptance of the concrete in a structure is the average of two 6” x 12” cylinders or three 4” x 8” cylinders.
The full test method outlines specifications around specimen preparation, curing, identification, loading, and calculating results. To follow ASTM C39, you will need concrete cylinder testing equipment.
Recommended Equipment for ASTM C39
Concrete Cylinder Specimen Preparation
To follow ASTM C39, cylindrical specimens must first be prepared and cured in accordance with:
- ASTM C31 (Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Field)
- ASTM C192 (Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory)
- ASTM C617 (Capping Cylindrical Concrete Specimens)
- ASTM C1231 (Use of Unbonded Caps in Determination of Compressive Strength of Hardened Cylindrical Concrete Specimens)
ASTM C31 specifies cylinders to be 6” x 12” or 4” x 8” inches, but it allows for variation depending on the project needs. The primary requirement is that the diameter of the cylinder is at least three times the nominal maximum size of the coarse aggregate. To prepare cylindrical specimens from a batch of fresh concrete at the job site in accordance with these ASTM standards, you will need:
- Cylinder molds: for shaping, setting and initial curing of the concrete
- Round mouth scoop: for filling the molds
- Tamping rod: for eliminating air voids in concrete cylinder preparation
- Strike-off bar: for removing excess material when molding cylinder specimens
- Rubber hammer: for releasing entrapped air in concrete molds

If you are in a scenario where you need to take a sample from in-place concrete as opposed to fresh concrete molds, you will need to be in accordance with ASTM C42 (Obtaining and Testing Drilled Cores and Sawed Beams of Concrete). This requires concrete coring equipment like:
- Core drilling machine: for extracting core samples from in-place concrete
- Extractor: for extracting cores from concrete after drilling
- Drill bits, clamps and expansion adapters as needed

Curing
Concrete curing is the process of keeping your concrete specimens at the proper moisture levels and temperature.
This involves curing equipment, including a concrete curing box or tank with heating and cooling elements.
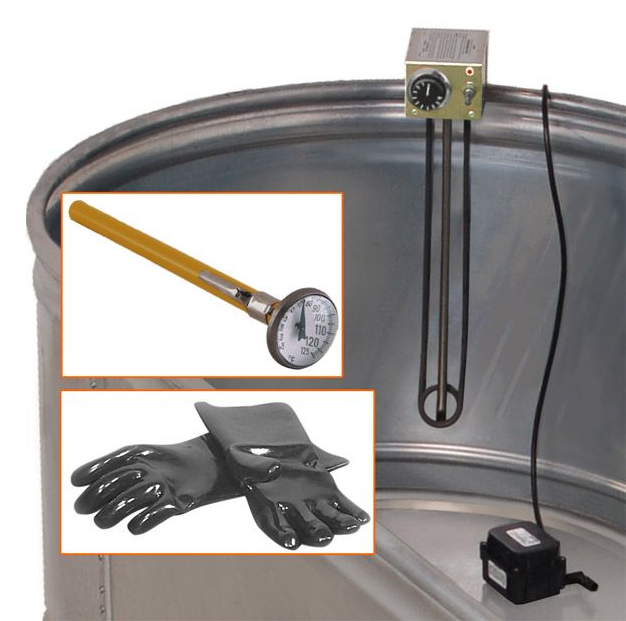

Strength Testing
To test the compressive strength of a concrete cylinder according to ASTM C39, you will need:
- Mold stripper: for removing the cured concrete cylinder from its mold
- Calipers: for measuring the diameter and height of the concrete cylinder
- Straight edge: for checking the planeness of the cylinder ends (ASTM C39 specifies that the difference in elevation between the ends of the cylinder should not exceed 0.002 inches over a 12-inch length)
- Grinding machine: for grinding the end of the cylinder to within the specified tolerance
- Capping equipment: to ensure the end of the cylinder is uniform so an even load can be applied.
- Pad caps: to ensure the end of the cylinder is uniform so an even load can be applied.
- Compression testing machine: for applying a gradual axial load to the concrete cylinder until it breaks

With all of the above concrete testing equipment, here’s how to follow the ASTM C39 test procedure and calculate results.
ASTM C39 Test Procedure & Results
Test Procedure
- Inspect the cylinders for defects, planeness, and perpendicularity.
- Saw, grind, or cap cylinders that do not meet the specified planeness tolerance to provide a uniform load distribution.
- Measure the diameter twice at the mid-height of each cylinder with the two measurements at right angles of each other, ensuring that the variance is less than two percent between them.
- Calculate the average diameter and surface area.
- Center the specimen on the lower platen of the compression testing machine.
- If using pad caps, verify vertical alignment of the cylinder in the machine.
- Apply a constant loading rate during the test, typically between 28 to 42 psi/s, to complete failure.
- Record break type.
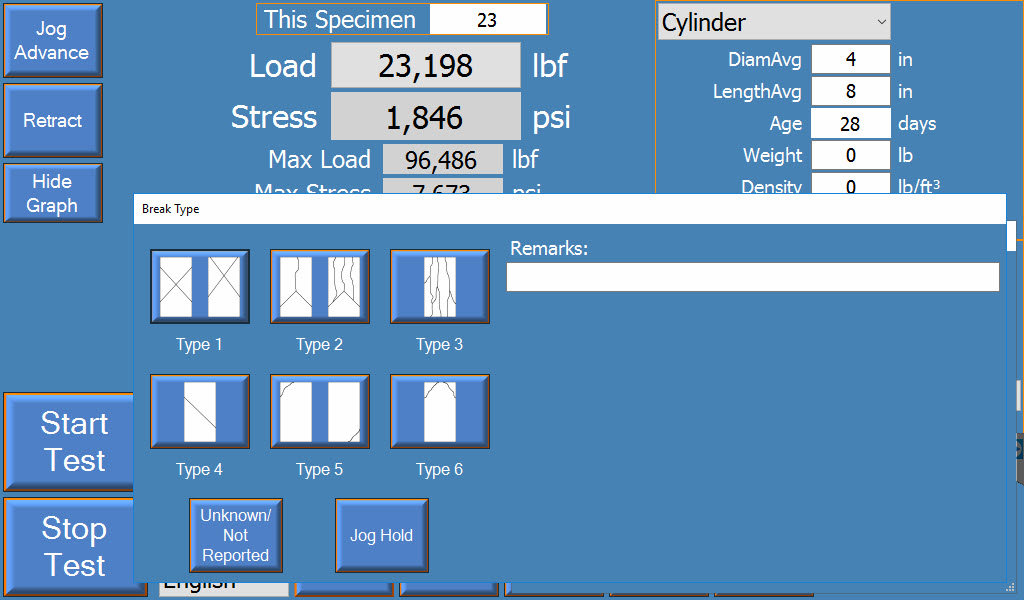
Results & Reporting
To calculate the strength of the concrete cylinder, divide the maximum load at failure by the average cross-sectional area.
ASTM C39 requires testers to report:
- Average measured diameter
- Cross-sectional area
- Test age
- Maximum load applied
- Compressive strength
- Type of fracture
- Defects in cylinder or caps
- Density to the nearest 1 lb/ft3
- Wet concrete data according to ASTM C31
During the compression test, technicians must manipulate the load at a constant rate. This is difficult to do on a manual machine, which is prone to human error and variability.
Because of this, more and more testers have upgraded to automatic testing machines to run ASTM C39. Automatic controls provide automatic preloading and rate adjustments, energy efficient hydraulics, higher test speeds within the allowable range, and consistency from operator to operator.
However, ASTM C39 also provides specific requirements for cylinder specimen identification to maintain traceability throughout the entire process. This includes marking cylinders with unique identifiers, recording relevant sample and set information, and following proper procedures for storing, handling and transporting specimens to testing locations.
While automatic machines help with the test itself, they do not have the context required for specimen identification. Connected CMT machines do.
Connected CMT machines combine the benefits of automatic testing with a native, two-way integration with CMT software. Before the test, the cylinder can be positively identified via barcode scan, and the compression machine will receive all the data associated with that cylinder to validate specimen geometry and calculate preload settings based on expected strength, age of the specimen, and history of the sample.
After the test, the connected machine will calculate compressive strength and transfer data automatically to your LIMS package, QC system, or other software. All to improve productivity, accuracy and transparency throughout the entire ASTM C39 test method.
Conclusion
ASTM C39 is a fundamental test method for measuring the compressive strength of concrete cylinders. Before performing ASTM C39, please be sure to reference the current ASTM standard.
Forney has the specialty compression machines, related accessories and software for ASTM C39. Shop the Forney store today or find your machine.
